Dynamically Provisioning Persistent Volumes
StorageClass
Storage Classes simplify the creation and management of Persistent Volumes by automatically provisioning storage resources whenever they are required. You can configure storage type like SSD or HDD, replication settings, and other configurations.
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: gcp-st
provisioner: kubernetes.io/gce-pd
parameters:
type: pd-ssd
- provisioner: Specifies the provision storage. We have used Google Cloud Persistent Disk kubernetes.io/gce-pd.
- parameters: pd-ssd is suitable for enterprise high-performance applications that require lower latency and more IOPS than standard persistent disks provide.
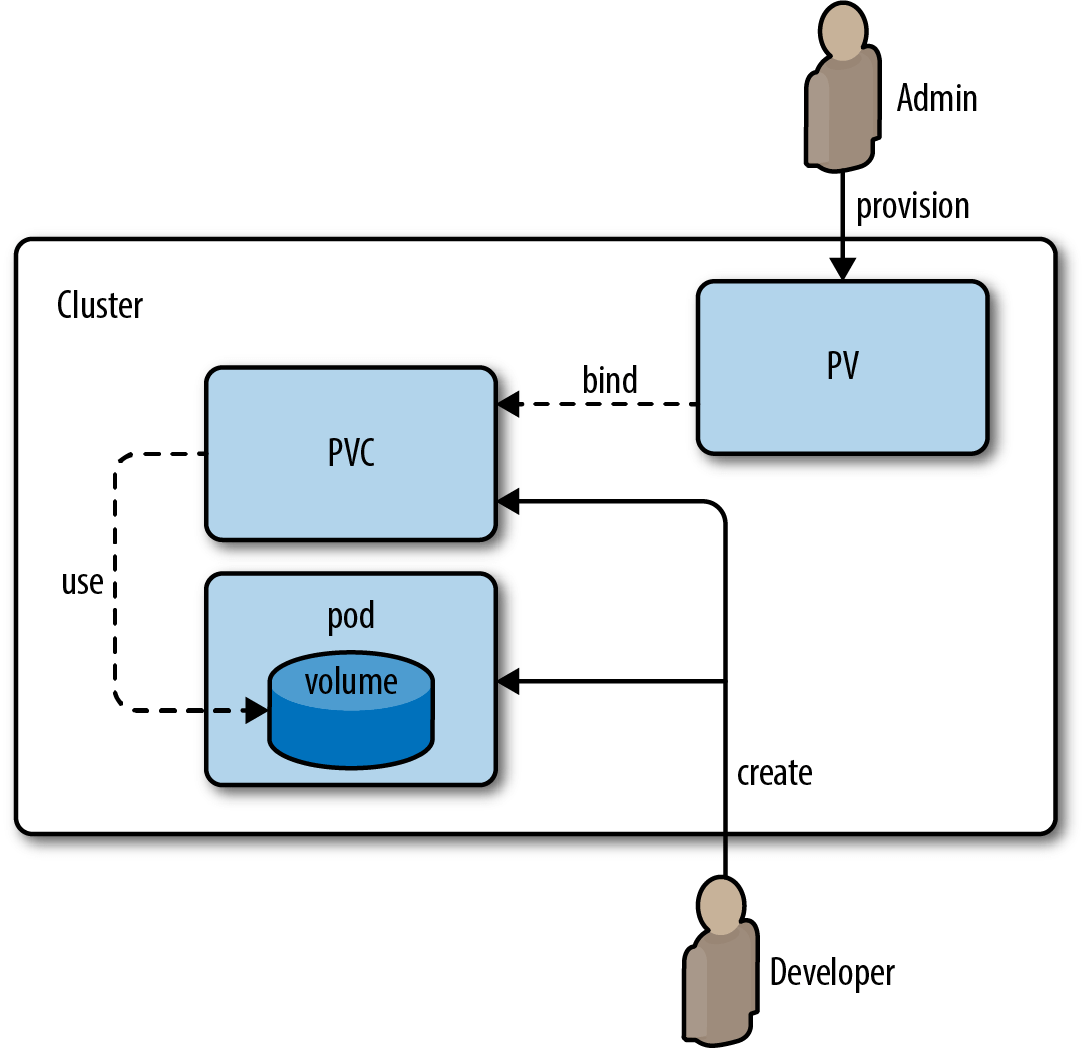
Persistent Volume Claim
A Persistent Volume Claim in Kubernetes is a request for storage by an application. It enables dynamic allocation of persistent volume in a cluster. Claims can request specific size and access volume by a Pod. When a PVC references a StorageClass It will trigger dynamic provisioning if no suitable Persistent Volume already exists.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: c-claim
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Mi
storageClassName: gcp-st
volumeMode: Filesystem
The storageClassName: gcp-st ensures that dynamic provisioning will use the gcp-std StorageClass we have defined earlier, which provisions storage on Google Cloud Persistent Disk with solid-state drives.
volumeMode: Filesystem or Block type is used as volumeMode where Filesystem is defined as a regular file system. On the other hand, if the volumeMode is Block, persistent volume will give access to raw storage that is useful for several applications that are using their own file system, like Kafka or a database.
PersistentVolumeClaim is used by Pod to mount storage. In the given pod’s specification, I have mounted /log path. with the volume claim c-claim.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: app
spec:
containers:
- image: cmabdullah21/log-simulation
name: log-simulation
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /log
name: application-log
volumes:
- persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: c-claim
name: application-log
If pod is lost, data will be preserved on the referenced volume.
by hitting this command
kubectl exec -it app – ls /log
You can check if the volume directory has been properly mounted within the pod.
